New Aquarium Water Setup: The Complete Guide to Proper Water Conditioning and Tank Cycling
Setting up a new aquarium is one of the most exciting moments for any fish enthusiast, but proper water conditioning and tank cycling are crucial for creating a healthy environment for your future fish. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of the process, ensuring your new aquarium is ready to support aquatic life safely and effectively.

Understanding the Aquarium Water Setup Process
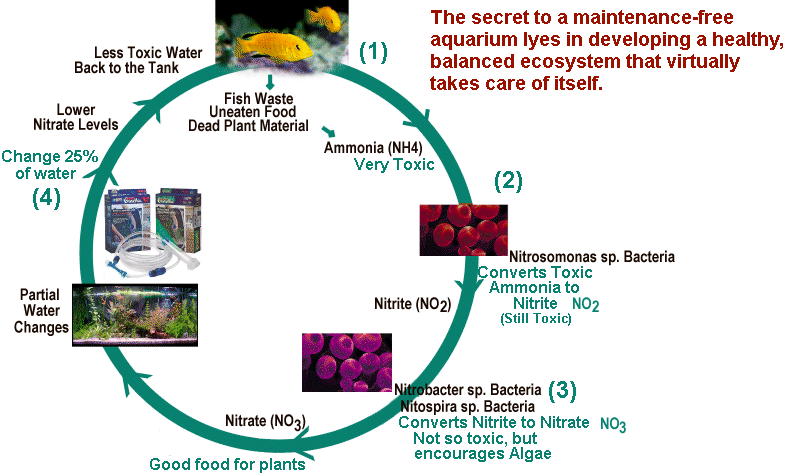
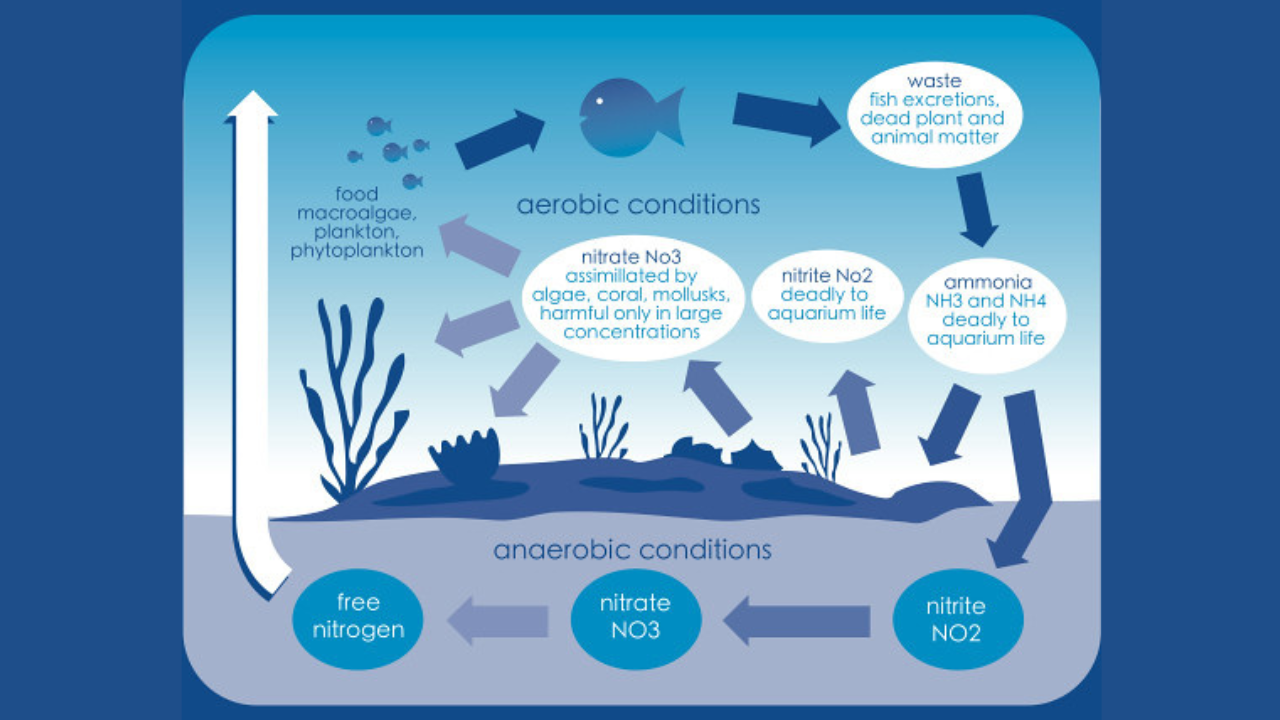
Before adding any fish to your new aquarium, you must establish a biological filtration system through a process called “cycling.” This involves growing beneficial bacteria that will convert toxic fish waste into less harmful compounds, creating a stable aquatic ecosystem.
What is Tank Cycling?
Tank cycling is the process of establishing colonies of beneficial nitrifying bacteria in your aquarium’s filter system and substrate. These bacteria are essential for converting:
- Ammonia (highly toxic) → Nitrite (also toxic) → Nitrate (relatively harmless)
This biological process, known as the nitrogen cycle, is fundamental to maintaining healthy water conditions for fish.
Step-by-Step New Aquarium Water Setup
Step 1: Initial Tank Preparation
Equipment Needed:
- Aquarium tank and stand
- Filtration system (appropriate for tank size)
- Heater (for tropical fish)
- Substrate (gravel or sand)
- Decorations and plants
- Water testing kit
- Water conditioner/dechlorinator
Setup Process:
- Clean everything thoroughly with warm water (no soap!)
- Install substrate – rinse until water runs clear
- Add decorations and hardscape before filling
- Install equipment (filter, heater, lights)

Step 2: Water Conditioning – The Critical First Step
Never add untreated tap water directly to your aquarium. Tap water contains chlorine and chloramines that are toxic to fish and will kill beneficial bacteria.
Water Conditioning Process:
- Fill your aquarium with tap water
- Add water conditioner according to package directions
- Treat the entire volume of your tank, not just new water
- Wait 15-30 minutes for complete dechlorination
- Test water parameters before proceeding
Essential Water Conditioners:
- Dechlorinators (removes chlorine/chloramines)
- Stress coat products (adds protective slime coat)
- pH adjusters (if needed for your fish species)
Water Conditioner Products
Step 3: Choosing Your Cycling Method
There are two primary methods for cycling a new aquarium:
Method 1: Fishless Cycling (Recommended)
Fishless cycling is the safest and most humane method, establishing beneficial bacteria without risking fish health.
Advantages:
- No fish are subjected to toxic ammonia/nitrite
- More predictable timeline
- Better bacterial establishment
- No emergency interventions needed
Process:
- Add ammonia source to empty tank
- Monitor water parameters daily
- Wait for bacterial colonies to establish
- Confirm cycle completion before adding fish
Method 2: Fish-In Cycling
Fish-in cycling uses hardy fish to provide ammonia for bacterial growth.
Advantages:
- Immediate fish presence
- Natural ammonia production
- Traditional method
Disadvantages:
- Risk of fish stress or death
- Requires constant monitoring
- Frequent water changes needed
- More expensive long-term
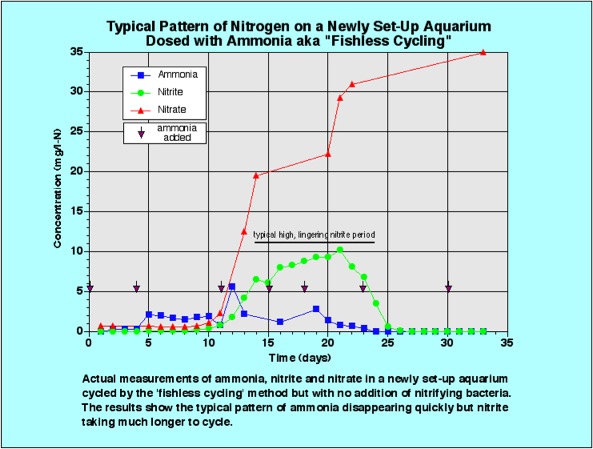
The Complete Fishless Cycling Process
Week 1-2: Ammonia Introduction
Day 1:
- Add water conditioner to treat full tank volume
- Add beneficial bacteria starter (recommended)
- Introduce ammonia source:
- Pure ammonia solution: 2-3 ppm concentration
- Fish food method: Small pinch daily
- Raw shrimp method: 1-2 pieces
Days 2-7:
- Test ammonia daily (should remain 2-3 ppm)
- Test nitrite daily (should be 0 initially)
- Add ammonia as needed to maintain levels
- No water changes during this phase
Week 2-4: Nitrite Spike Phase
What to Expect:
- Ammonia begins converting to nitrite
- Nitrite levels rise significantly
- Ammonia levels may decrease
- Water may become cloudy (bacterial bloom – normal!)
Monitoring Protocol:
- Test ammonia and nitrite every 2-3 days
- Continue adding ammonia in smaller doses
- Keep nitrite below 5 ppm to avoid bacterial poisoning
- Patience is key – this phase can take 2-3 weeks

Week 4-6: Cycle Completion
Signs of Cycle Completion:
- Ammonia drops to 0 ppm within 24 hours of dosing
- Nitrite drops to 0 ppm within 24 hours
- Nitrate levels increase (5-20 ppm is normal)
- Water clears up from bacterial bloom
Final Confirmation Test: Add full ammonia dose and test after 24 hours:
- ✅ Ammonia: 0 ppm
- ✅ Nitrite: 0 ppm
- ✅ Nitrate: Present (5-20 ppm)
If results match above, your tank is cycled!
Accelerating the Cycling Process
Using Commercial Bacterial Supplements
Recommended Products:
- DrTim’s One & Only Live Bacteria
- API Quick Start
- Seachem Stability
- Fluval Biological Enhancer
Benefits:
- Reduces cycling time to 7-14 days
- Provides live beneficial bacteria
- More reliable than natural cycling
- Safer for fish-in cycling
API Quick Start Bottle
Seeding from Established Aquariums
Methods:
- Filter media transfer: Move sponge/bio-media from cycled tank
- Substrate addition: Add handful of gravel from established tank
- Water transfer: Limited benefit (bacteria live on surfaces)
Important: Only use materials from healthy, disease-free tanks
Water Parameter Management During Cycling
Essential Test Parameters
Primary Tests:
- Ammonia: Should be 0 ppm after cycling
- Nitrite: Should be 0 ppm after cycling
- Nitrate: 5-40 ppm acceptable (under 20 ppm ideal)
- pH: Species-dependent (6.5-8.0 for most fish)
Secondary Tests:
- Temperature: Consistent for species requirements
- Hardness (GH/KH): Species-dependent
- Dissolved oxygen: Ensure adequate surface agitation
Managing Problem Parameters
High Ammonia/Nitrite During Cycling:
- Reduce feeding (fish-in cycling)
- Increase surface agitation
- Add beneficial bacteria supplement
- Consider partial water changes if extreme
pH Fluctuations:
- Test and adjust gradually
- Use buffering substrates if needed
- Monitor after water changes
Common Mistakes to Avoid — 피해야 할 일반적인 실수
Critical Errors in New Tank Setup
1. Adding Fish Too Early
- Mistake: Adding fish before cycle completion
- Consequence: Fish stress, illness, or death
- Solution: Complete full cycling process first
2. Inadequate Water Conditioning
- Mistake: Skipping dechlorinator or using insufficient amounts
- Consequence: Chlorine kills beneficial bacteria and fish
- Solution: Always treat full tank volume
3. Impatience with Cycling Process
- Mistake: Rushing the timeline or adding too many fish at once
- Consequence: Ammonia/nitrite spikes, system crash
- Solution: Follow proper timeline and stock gradually
4. Incorrect Ammonia Levels
- Mistake: Adding too much or too little ammonia
- Consequence: Poor bacterial establishment or toxicity
- Solution: Maintain 2-3 ppm consistently
:strip_icc()/common-new-aquarium-mistakes-1380712_FINAL-e4b82ab20a254a5b8d7b9ca09a56d665.png)
Different Approaches for Different Aquarium Types
Freshwater Community Tanks
Setup Priorities:
- Stable pH (6.8-7.5)
- Moderate hardness
- Consistent temperature (75-78°F)
- Adequate filtration for bioload
Cycling Time: 4-6 weeks (2-3 weeks with bacteria supplement)
Saltwater Aquariums
Additional Considerations:
- Salinity management (specific gravity 1.020-1.025)
- Higher pH requirements (8.1-8.4)
- More complex chemistry
- Longer cycling period
Cycling Time: 6-8 weeks (3-4 weeks with live rock)
Planted Aquariums
Special Requirements:
- CO2 considerations during cycling
- Plant establishment before fish
- Substrate choices affect cycling
- Lighting schedules during establishment
Cycling Time: 3-4 weeks (plants help process ammonia)
Introducing Fish After Cycling
Gradual Stocking Protocol
Week 1: Add 25% of planned fish load Week 2: Monitor parameters, add another 25% Week 3: Continue monitoring, add remaining fish gradually Week 4+: Full bioload established
Proper Fish Acclimation
Temperature Acclimation:
- Float sealed bag in tank for 15-20 minutes
- Gradually add tank water to bag over 30 minutes
- Net fish into tank (avoid adding bag water)
Quarantine Considerations:
- Separate quarantine tank recommended
- 2-4 week observation period
- Treat for common parasites/diseases

Troubleshooting Common Cycling Problems
Cycle Stalls or Fails to Progress
Possible Causes:
- pH too low (below 6.5)
- Temperature too cold (below 65°F)
- Insufficient aeration
- Chlorine/chloramine poisoning
- Wrong ammonia type
Solutions:
- Test and adjust pH to 7.0-8.0
- Increase temperature to 75-80°F
- Add air stone or increase filter flow
- Add more dechlorinator
- Use pure ammonia source only
Bacterial Blooms and Cloudy Water
Normal Response:
- Cloudy white water is normal during cycling
- Indicates healthy bacterial growth
- Usually clears within 3-7 days
- Do not change water unless parameters are dangerous
When to Worry:
- Green water (algae bloom – different issue)
- Foul odors (anaerobic conditions)
- Extremely high ammonia (over 8 ppm)
Mini-Cycles After Adding Fish
What it Means:
- Normal response to increased bioload
- Indicates system adjusting to new fish
- Should resolve within 3-5 days
Management:
- Monitor parameters closely
- Reduce feeding temporarily
- Add beneficial bacteria supplement
- Consider small water change if parameters spike
Long-Term Maintenance After Setup
Regular Testing Schedule
First Month:
- Test daily for ammonia/nitrite
- Weekly tests for nitrate/pH
- Monitor fish behavior closely
Established Tank:
- Weekly ammonia/nitrite checks
- Bi-weekly nitrate/pH testing
- Monthly comprehensive testing
Water Change Protocol
Frequency:
- New tanks: 10-15% weekly
- Established tanks: 20-25% weekly
- Always match temperature and condition new water
Procedure:
- Test parameters before change
- Remove water from tank
- Condition replacement water
- Add slowly to avoid shocking fish
- Test parameters after change
Expert Tips for Success
Patience is Essential
Remember:
- Quality cycling takes time
- Rushing leads to problems
- Healthy bacteria colonies need 4-6 weeks minimum
- Each tank is unique in timing
Documentation Helps
Keep Records of:
- Daily parameter readings
- Feeding schedules
- Water change dates
- Fish additions
- Any problems and solutions
Plan for Different Scenarios
Have Ready:
- Extra dechlorinator
- Beneficial bacteria supplement
- Emergency medications
- Backup aeration system
- Hospital/quarantine tank setup
Conclusion
Proper new aquarium water setup and cycling is the foundation of successful fishkeeping. While the process requires patience and attention to detail, following these guidelines will ensure your aquarium provides a healthy, stable environment for your fish to thrive.
